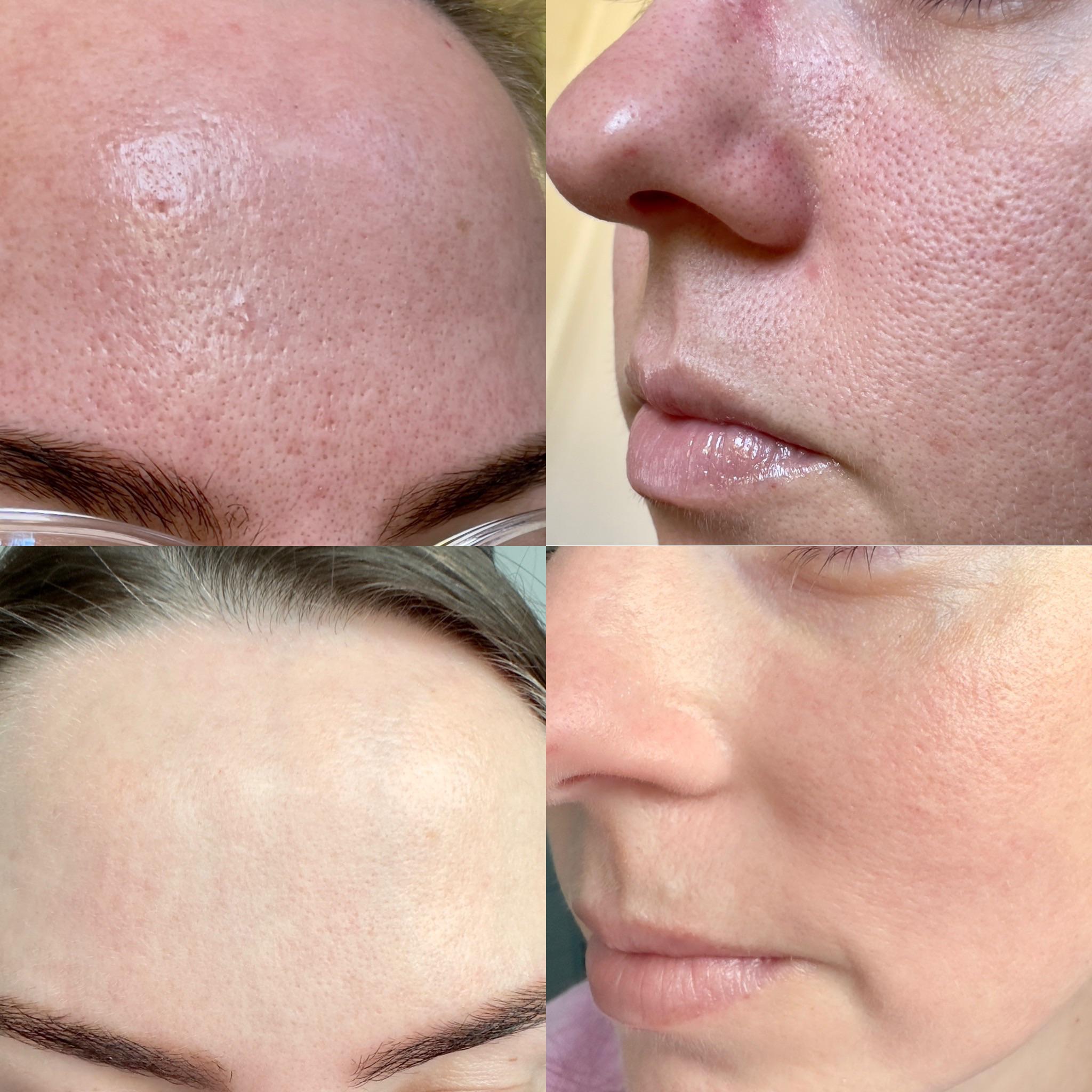
Consider a low-dose long-term treatment with Accutane for managing stubborn acne. Studies suggest that maintaining a lower dosage can minimize side effects while still achieving significant improvement in skin condition. Patients often report a transition to clearer skin over extended periods, leading to enhanced self-esteem and overall wellbeing.
Many dermatologists recommend a dose of 10 to 20 mg per day, which can be effective for prolonged durations. This approach helps in maintaining lower blood levels of the medication, reducing risks associated with higher doses, such as liver damage or severe dry skin. Regular monitoring of liver function tests and lipid levels is crucial to ensure safety and efficacy.
The benefits of long-term Accutane extend beyond just acne; they can include decreased oil production and lower incidence of future breakouts. Implementing a consistent skincare routine alongside this treatment can further enhance results. Incorporating a gentle cleanser and a hydrating moisturizer creates a balanced regimen, promoting skin health while minimizing irritation.
Keep an open dialogue with your healthcare provider to tailor the treatment plan to your specific needs. This ensures an optimal response while addressing any side effects that may occur during the process. Remember, gradual adjustments and routine check-ins can significantly contribute to the success of your low-dose Accutane journey.
- Low Dose Long Term Accutane: A Practical Guide
- Understanding the Mechanism of Low Dose Accutane in Acne Treatment
- Evaluating the Long Term Benefits and Risks of Low Dose Accutane
- Benefits of Low Dose Accutane
- Risks Associated with Low Dose Accutane
- Best Practices for Monitoring Patients on Long Term Low Dose Accutane
Low Dose Long Term Accutane: A Practical Guide
Begin treatment with a low dose of Accutane, around 10-20 mg per day. This approach reduces side effects while still providing effective acne management. Regular blood tests are crucial to monitor liver function and lipid levels throughout the course.
Stay hydrated. Accutane can cause dryness, so drink plenty of water and use moisturizers for skin and lips. Consider a humidifier in your living space to maintain skin moisture levels. Sunscreen is essential, as skin becomes more sensitive to sun exposure. Choose a high SPF product.
Connect with your dermatologist frequently. Schedule check-ups every month to discuss progress and any concerns. Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on examination results and feedback.
Implement a gentle skincare routine. Opt for non-comedogenic and alcohol-free products. Avoid harsh exfoliants or astringents to prevent irritation. Introduce new products slowly to assess their effects on your skin.
| Dosage (mg/day) | Expected Duration (months) | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| 10-20 | 6-12 | Dryness, chapped lips, increased sun sensitivity |
| 20-40 | 4-8 | Joint pain, possible mood changes |
Be mindful of mental health. Some users report mood swings during treatment. Journaling can help track emotions and discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional. Surround yourself with supportive individuals during this time.
Maintain a balanced diet. Including fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can aid overall skin health. Limit processed foods and sugar intake, which might exacerbate acne. Explore supplements like Omega-3 fatty acids under professional guidance.
Stay informed about potential long-term effects. Research indicates low-dose treatment can lead to lasting improvements in skin condition. Regular follow-ups after treatment completion help in monitoring any residual issues.
Consider maintenance options post-treatment. Consult your dermatologist about topical retinoids or low-dose oral antibiotics to sustain results. Lifestyle changes such as stress management techniques can also support skin health.
Understanding the Mechanism of Low Dose Accutane in Acne Treatment
Low dose isotretinoin, commonly known as Accutane, significantly reduces acne by targeting the underlying causes. It acts directly on sebaceous glands to decrease oil production, which is crucial since excess sebum contributes to acne formation. By reducing oil, the likelihood of clogged pores diminishes, leading to fewer breakouts.
This medication also has anti-inflammatory properties. By lowering inflammation, isotretinoin helps to calm existing acne lesions, making them less noticeable and promoting faster healing. The drug influences the immune response, which aids in reducing the severity of acne that often results from bacterial growth.
Low doses minimize side effects while maintaining efficacy. Patients often experience fewer adverse reactions, such as dry skin or mood changes, compared to higher doses. Maintaining a long-term regimen allows for consistent monitoring and adjustment based on individual responses, creating a tailored treatment approach for acne management.
Additionally, isotretinoin affects keratinization, a vital process in skin cell turnover. By normalizing keratinization, it prevents the formation of comedones (clogs) that lead to acne. This alteration helps keep pores clear over time, contributing to a sustained reduction in acne lesions.
Overall, low dose Accutane offers a balanced strategy for treating acne, focusing on oil production, inflammation, and skin cell turnover. By choosing this approach, patients may achieve clearer skin with a reduced risk of significant side effects, making it an appealing option for long-term management.
Evaluating the Long Term Benefits and Risks of Low Dose Accutane
Low dose Accutane presents a compelling option for individuals managing persistent acne. Research indicates that this approach can yield significant long-term benefits while mitigating some risks associated with higher doses.
Benefits of Low Dose Accutane
- Reduced Acne Recurrence: Studies show that low doses may lead to prolonged remission from acne, often lasting years after treatment.
- Lower Side Effects: Patients generally experience fewer severe side effects compared to standard doses, making treatment more tolerable.
- Improved Skin Quality: Lower dosages can enhance skin texture and decrease oiliness without excessive dryness or irritation.
- Convenient Treatment Duration: Extended treatment periods at lower doses can be effective, allowing time for gradual skin improvement.
Risks Associated with Low Dose Accutane
- Potential for Incomplete Response: Some individuals may not achieve full clearance of acne, requiring alternative treatments.
- Continuous Monitoring Needed: Regular evaluations are essential to assess liver function and lipid levels due to potential drug-related impacts.
- Emotional Effects: Although less common, some patients might still experience mood changes, requiring psychological support during treatment.
Balancing benefits and risks plays a key role in making informed treatment decisions. Consulting with a dermatologist ensures personalized strategies tailored to individual needs. Regular follow-ups and communication help address concerns, optimizing the overall treatment experience. Individuals should stay informed and proactive in their skincare journey for the best possible outcomes.
Best Practices for Monitoring Patients on Long Term Low Dose Accutane
Regular laboratory tests are crucial. Schedule blood tests every month for the first 6 months, then every 3 months thereafter. Monitor liver function tests and lipid levels, as isotretinoin can elevate liver enzymes and triglycerides.
Assess for side effects consistently. Patients should report any unusual symptoms, especially mood changes, joint pain, and visual problems. Create an open channel for communication, encouraging them to voice concerns promptly.
Provide education on potential side effects. Discuss dry skin, mucous membranes, and potential for photosensitivity. Suggest using moisturizers and sunscreen to mitigate these effects.
Ensure pregnancy prevention is a priority. Advise female patients to use two forms of contraception during treatment and continue its use for a month after discontinuation. Confirm negative pregnancy tests before starting and each month during treatment.
Encourage regular follow-ups. Schedule appointments at least every three months to evaluate treatment progress and any emerging issues. Discuss adherence to the regimen, and address any barriers that patients might encounter.
Maintain a comprehensive record of each patient’s treatment history. This includes dosages, lab results, and reported side effects to ensure informed management and adjustments as needed.
Foster a collaborative relationship. Engage patients in their treatment plans by discussing goals and expectations. This cooperation can enhance adherence and overall satisfaction with the treatment process.
Consider mental health screenings. Given the associations between isotretinoin and mood changes, assess mental health at baseline and throughout treatment. This will help identify any issues early and allow for timely interventions.