The typical dosage of prednisone for hives starts at 20 to 40 mg per day. This initial amount is often prescribed for a short period, typically 5 to 10 days, to quickly reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Dosages may vary based on individual reactions and the severity of the hives.
After the first few days, your doctor may adjust the dosage, gradually tapering it down. The goal is to find the lowest effective dose that provides relief while minimizing side effects. Consultation with a healthcare provider ensures that adjustments are safe and appropriate for your specific condition.
Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions on how to take prednisone. Avoid altering the dose or discontinuing the medication without professional guidance, as this can lead to complications. Monitoring your symptoms closely during treatment will help you and your provider make informed decisions about your care.
- How Much Prednisone for Hives
- Understanding Hives and Their Causes
- Common Triggers of Hives
- Understanding the Immune Response
- Recommended Dosage of Prednisone for Hives
- Adjusting Dosage
- Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage
- Potential Side Effects of Prednisone for Hives
- When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
How Much Prednisone for Hives
The typical dosage of prednisone for treating hives ranges from 20 mg to 60 mg per day, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the individual patient’s response. Your doctor may prescribe a higher initial dose for rapid relief, tapering down the dosage as symptoms improve.
For mild cases, starting with 20-30 mg daily may suffice. In more severe situations, 40-60 mg might be appropriate. Always follow your healthcare provider’s precise recommendations, as they consider your medical history and potential interactions with other medications.
Treatment duration typically lasts from a few days to a week. Prolonged use of prednisone can lead to significant side effects. Monitor for any changes in your health and report them to your doctor immediately.
After the initial treatment, your doctor may suggest a gradual reduction in dosage to minimize withdrawal symptoms and rebound reactions. Always consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen.
Understanding Hives and Their Causes
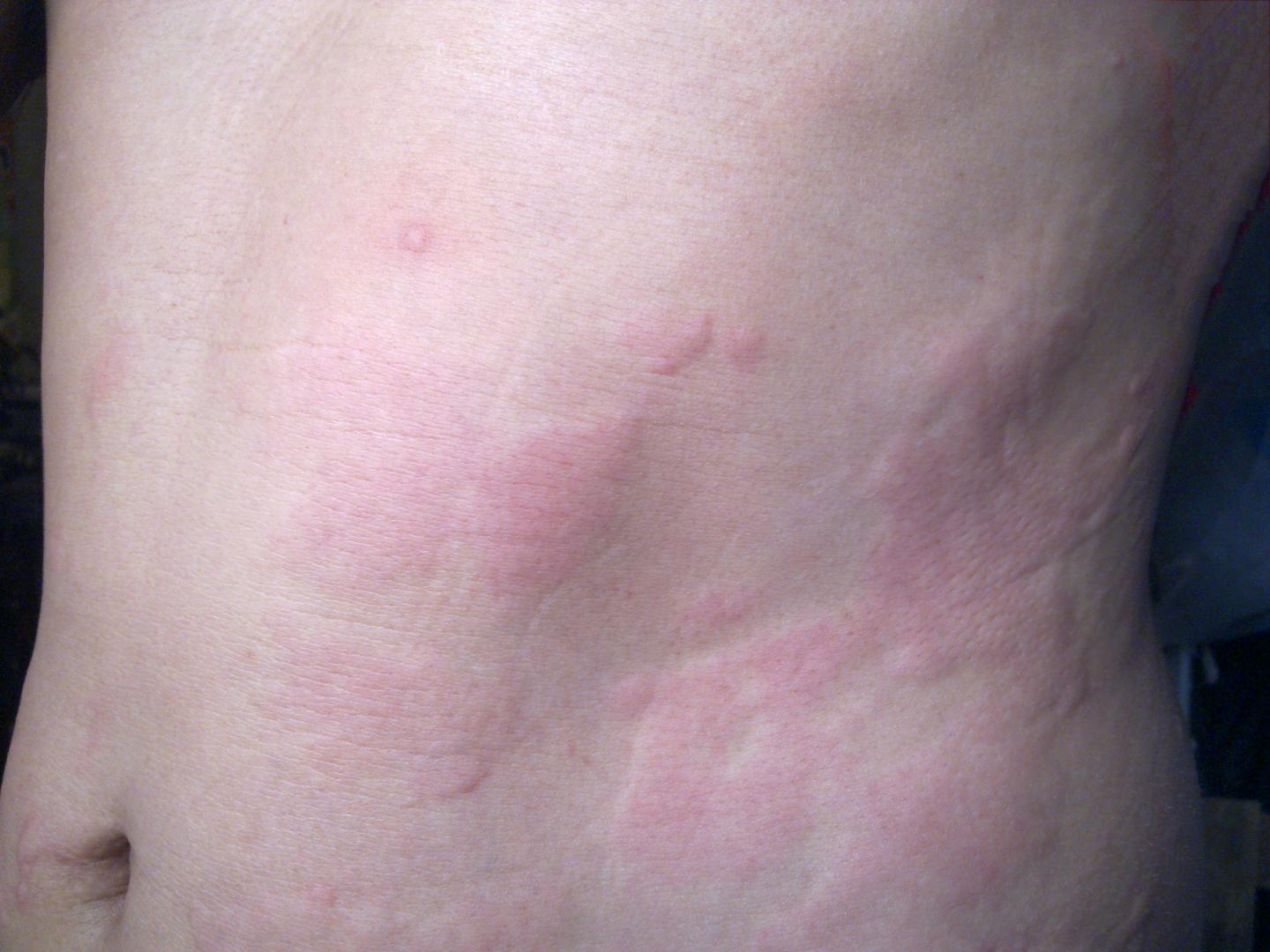
Hives, or urticaria, appear as raised, itchy welts on the skin, often resulting from an allergic reaction. Understanding their triggers helps manage symptoms effectively.
Common Triggers of Hives
- Foods: Shellfish, nuts, eggs, and dairy frequently cause allergic reactions.
- Medications: Antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and some vaccines can trigger hives.
- Insect Stings: Reactions to bee or wasp stings may manifest as hives.
- Environmental Factors: Pollen, pet dander, and latex are common allergens that provoke hives.
- Physical Stimuli: Pressure, temperature changes, or sunlight can induce hives in some individuals.
Understanding the Immune Response
When the body encounters an allergen, it releases histamines as part of the immune response. Histamines cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to swelling and redness. Identifying and avoiding triggers can significantly reduce outbreaks. Keeping a diary of food intake, medications, and exposure to environmental factors assists in pinpointing specific causes.
Consult a healthcare provider for targeted allergy testing if hives persist. They can recommend treatment options, including antihistamines, to alleviate symptoms effectively.
Recommended Dosage of Prednisone for Hives
The typical dosage of prednisone for treating hives ranges from 20 mg to 60 mg daily, based on severity. For mild cases, starting with 20 mg may be sufficient, while moderate to severe cases often require higher doses. Treatment duration usually lasts from 5 to 10 days, with doctors advising tapering the dose to minimize potential side effects.
Adjusting Dosage
Your healthcare provider may adjust the dosage depending on your response to treatment and any side effects you experience. It’s critical to follow your provider’s instructions closely, as individual needs can vary significantly.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage
The dosage of prednisone for managing hives varies based on several key factors. Individual health conditions significantly impact the appropriate dosage. For adults, a typical starting dose might range from 20 to 60 mg per day, but this can be adjusted based on medical history.
Weight also plays a crucial role. Heavier individuals may require higher doses to achieve the desired effect, while those who weigh less often respond well to lower amounts. Age is another factor; older adults may be more sensitive to corticosteroids, necessitating careful dosage adjustments.
Duration of hives affects the treatment plan. Acute cases might respond swiftly to lower doses, while chronic conditions may require higher dosages over a longer period. Underlying health issues, such as adrenal insufficiency or infections, can alter how one metabolizes prednisone, leading to different dosage recommendations.
Concurrent medications should also be considered, as some drugs can interact with prednisone, changing its efficacy or safety. Monitoring response to treatment allows healthcare providers to adjust the dosage for optimal relief.
A healthcare professional’s guidance remains essential in tailoring the prednisone dose for each individual, ensuring the most suitable and effective treatment approach for hives.
Potential Side Effects of Prednisone for Hives
Prednisone can help manage hives effectively, but it comes with possible side effects. Common reactions include increased appetite, weight gain, and mood changes. Some individuals may experience insomnia or restlessness, which can disrupt daily life.
Gastrointestinal issues, such as stomach upset, can occur. Taking prednisone with food may help alleviate these symptoms. Prolonged use might lead to more serious effects like increased blood sugar levels, which is particularly relevant for those with diabetes.
Osteoporosis becomes a concern with long-term use, as prednisone can weaken bones. Regular monitoring of bone density is advisable if using this medication over extended periods. Additionally, individuals may notice a higher susceptibility to infections, as prednisone suppresses the immune system.
Some patients experience skin changes, including acne or thinning skin, which may be distressing. It’s essential to monitor these effects and discuss them with your healthcare provider to adjust treatment as necessary.
For those considering or currently using prednisone for hives, staying informed about these side effects enhances overall safety and helps maintain well-being during treatment.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If hives persist for more than a few days or frequently recur, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation. Seek medical advice immediately if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or signs of anaphylaxis, such as rapid heartbeat or dizziness. These symptoms may indicate a severe allergic reaction requiring urgent care.
If over-the-counter antihistamines do not alleviate your symptoms, a healthcare provider can recommend appropriate treatments, including possible prednisone use. Discuss any other medications you are taking, as interactions may affect treatment options. It’s also important to consult if you notice hives accompanied by a fever or joint pain, as these could indicate an underlying health issue.
Maintain open communication with your healthcare professional about any recent changes in your diet, medications, or environment that may have triggered your hives. Understanding potential allergens can aid in prevention and management strategies. Regular follow-ups may help to monitor your condition and adjust treatment plans as needed.