Toradol, with its active ingredient ketorolac, typically remains in your system for up to 24 hours after the last dose. The medication is eliminated through the kidneys, and individuals with kidney impairment may experience a longer duration in their system.
On average, the half-life of Toradol ranges from 5 to 6 hours, meaning it takes this time for half of the drug to be eliminated. For those taking multiple doses, the accumulation of the drug may lead to detectable levels for an extended period.
Drug tests for Toradol are not common, but its metabolites can be identified in urine for up to 72 hours post-administration. If you have a planned procedure or a drug test, staying mindful of these timelines is beneficial. Always consult a healthcare professional regarding your specific situation for personalized advice.
- How Long Does Toradol Stay in System
- Factors Affecting Duration
- Detection Times
- Understanding Toradol and Its Uses
- How Toradol Works
- Administration and Dosage
- Pharmacokinetics of Toradol
- Absorption and Distribution
- Metabolism and Elimination
- Factors Affecting Toradol Clearance
- Testing Methods for Toradol Detection
- Duration of Toradol Effects on the Body
- Implications for Patients Undergoing Surgery
- Monitoring Recovery
- Communication with Healthcare Providers
- Advice for Safe Use of Toradol
- Dosage Guidelines
- Monitoring Your Health
How Long Does Toradol Stay in System
Toradol (ketorolac) typically remains in the system for about 24 to 48 hours after the last dose. The duration varies based on factors such as dosage, duration of use, and individual metabolism. It’s important to be aware of these variables when considering Toradol’s presence in your body.
Factors Affecting Duration
Multiple factors influence how long Toradol stays in the system:
- Dosing: Higher doses increase the time it takes for the drug to be eliminated.
- Frequency of Use: Extended use can lead to accumulation in the body.
- Metabolism: Individual differences in metabolism can affect clearance rates.
- Age and Health: Older adults and those with kidney issues may experience prolonged effects.
Detection Times
For those subject to drug testing, Toradol is typically undetectable after 48 hours. However, detection times can vary based on testing methods and the individual’s physical condition.
| Factor | Impact on Duration |
|---|---|
| Dosage | Higher doses increase duration. |
| Duration of Use | Long-term use can extend presence in the system. |
| Metabolism | Quicker metabolism reduces duration. |
| Age | Older age may prolong elimination time. |
If you have specific concerns about Toradol and its effects, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended. They can provide tailored advice based on your personal health history and circumstances.
Understanding Toradol and Its Uses
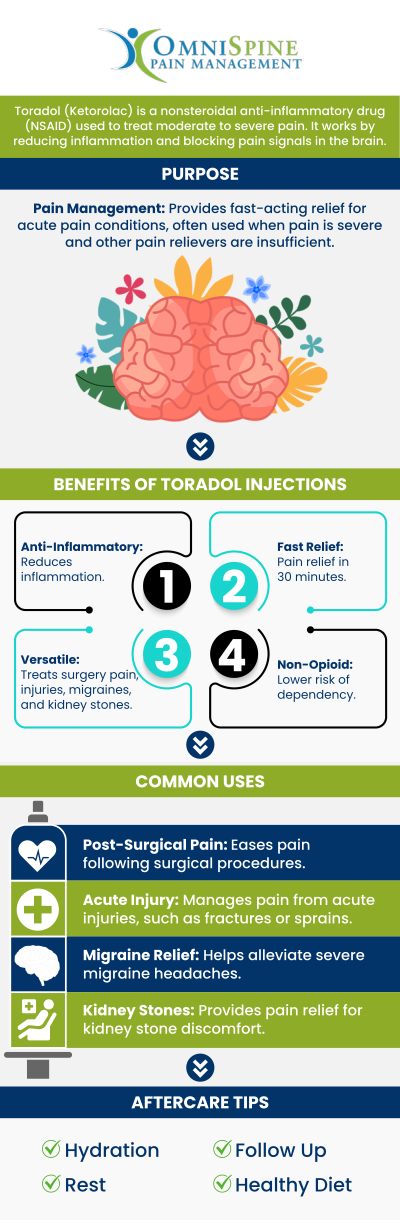
Toradol, or ketorolac, serves as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly prescribed for short-term relief of moderate to severe pain. Medical professionals often recommend it following surgeries, injuries, or for conditions like kidney stones. Its potency makes it a preferred choice when patients require effective pain management without the use of stronger opioids.
How Toradol Works
Toradol functions by inhibiting certain enzymes in the body, specifically cyclooxygenase (COX), which play a crucial role in the production of prostaglandins. These compounds contribute to inflammation and pain sensation. By diminishing their production, Toradol effectively reduces pain and inflammation.
Administration and Dosage
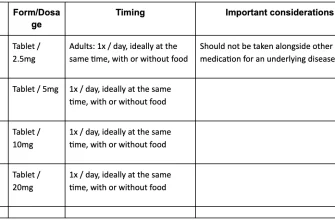
This medication can be administered via injection or taken orally, depending on the patient’s needs and the clinical setting. Typically, for adults, healthcare providers recommend a short course, usually not exceeding five days, to limit the risk of side effects. It’s essential to follow dosage instructions carefully and consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Pharmacokinetics of Toradol
Toradol (ketorolac) has specific pharmacokinetic properties that significantly influence its therapeutic efficacy and duration of action. Administered either orally or via injection, Toradol exhibits a rapid onset of action, typically between 30 minutes to an hour, which allows for swift pain relief.
Absorption and Distribution
When taken orally, Toradol’s bioavailability ranges from 80% to 100%. This high absorption rate means that a standard dose can quickly enter the bloodstream. Once absorbed, ketorolac distributes widely throughout body tissues, reaching higher concentrations in areas with acute inflammation.
- Peak plasma concentrations occur approximately 2 to 3 hours post-administration for the oral form.
- Intramuscular injections lead to quicker peak plasma levels, typically within 30 minutes.
Metabolism and Elimination
Ketorolac undergoes hepatic metabolism, primarily through conjugation. The drug is gradually transformed into inactive metabolites before elimination. The half-life of Toradol in healthy adults ranges from 5 to 10 hours, which influences dosing frequency.
- Renal impairment affects the elimination of Toradol, necessitating dose adjustments.
- Avoid prescribing Toradol for extended periods, typically limited to 5 days, due to potential side effects and risk of accumulation.
Understanding the pharmacokinetics of Toradol helps in optimizing its use and ensuring safety during treatment. Regular monitoring, particularly in patients with renal concerns, is recommended to prevent adverse effects while achieving effective pain management.
Factors Affecting Toradol Clearance
The clearance of Toradol (ketorolac) from the body can vary based on several key factors. Understanding these factors can help gauge how long the medication remains effective and detectable in the system.
Age plays a significant role in clearance rates. Older adults may experience slower clearance due to decreased liver and kidney function. Adjusting the dosage for this population is often necessary to avoid accumulation and potential side effects.
Body weight also affects how Toradol is processed. Individuals with higher body mass may require different dosing schedules, as the drug could distribute differently in body tissues.
Existing renal and hepatic function directly influences Toradol clearance. Impaired kidney function can lead to prolonged effects, as this drug is largely eliminated through the kidneys. Regular monitoring of renal function is advisable when prescribing Toradol to patients with known kidney issues.
Co-administration of other medications impacts Toradol metabolism. Drugs that affect liver enzymes can either speed up or delay the clearance of Toradol. Always inform healthcare providers of all medications being taken to adjust treatment plans effectively.
Lastly, hydration levels can influence clearance. Dehydration may exacerbate renal function, delaying elimination. Staying well-hydrated supports optimal drug processing and enhances safety during Toradol use.
Testing Methods for Toradol Detection
Detection of Toradol (ketorolac) in the body primarily utilizes urine and blood tests. Urine testing remains the most common method due to its non-invasive nature and longer detection windows.
Standard urine tests can identify Toradol use for up to 48 hours post-administration. However, advanced techniques, like gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), can accurately detect lower concentrations and may extend the detection period.
Blood tests offer a more immediate assessment, determining whether Toradol is currently in the system. These are often used in clinical settings or when rapid results are necessary. Blood tests can typically detect Toradol within hours after consumption, but their short detection window means they are less effective for extended monitoring.
Saliva tests represent another alternative, allowing for quick screening and detection. Although less common, they can identify recent use and function effectively in scenarios where urine testing is not feasible.
Hair testing is less practical for Toradol detection due to its metabolization process but can theoretically reveal past usage over several months, making it less reliable for immediate assessment.
Choosing the right testing method depends on the required detection timeframe and the context of the testing. Each method has its advantages, and the decision will hinge on the specific needs of the situation, such as compliance monitoring or medical diagnostics.
Duration of Toradol Effects on the Body
Toradol, or ketorolac, typically maintains its effects in the body for a duration of 4 to 6 hours following administration. After this period, its analgesic effects begin to diminish significantly. This timeframe allows for effective pain relief without the necessity for frequent dosing.
The elimination half-life of Toradol is approximately 5 to 6 hours in healthy adults. This means that after this period, half of the drug is no longer active in the system. However, certain factors such as age, liver function, and kidney function can influence how long the drug stays in the body.
In general, patients experience the peak effects of Toradol about 1 to 2 hours post-injection. After this peak, users can expect a gradual decline in pain relief as the drug is metabolized and excreted. For those taking Toradol for chronic conditions, doctors often recommend scheduling doses to maintain consistent pain control without overlapping into prolonged use.
Always adhere to prescribed dosages to avoid complications such as gastrointestinal bleeding or renal impairment, which can arise from prolonged use. It’s advisable to discuss any concerns about dosing or duration with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and efficacy.
If you require ongoing pain management, consider consulting a doctor for alternative therapies that may provide longer-lasting relief. Understanding the specific properties and duration of Toradol helps in making informed decisions about pain management strategies.
Implications for Patients Undergoing Surgery
Patients should discontinue Toradol at least 24 hours before scheduled surgery. This nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) can interfere with platelet function, raising the risk of bleeding during and after the procedure. It’s essential to discuss all medications, including over-the-counter options, with your surgical team in advance.
Monitoring Recovery
After surgery, your healthcare provider will monitor your recovery closely, especially if you had taken Toradol previously. Some patients might require alternative pain management strategies to reduce complications linked to bleeding or delayed healing. Always follow post-operative instructions regarding medication use to ensure an optimal recovery process.
Communication with Healthcare Providers
Maintain open communication with your doctors regarding any pain management preferences and concerns about Toradol use. Sharing your complete medication history allows for personalized care tailored to your unique needs, minimizing risks associated with any surgical procedure.
Advice for Safe Use of Toradol
Always consult with your healthcare provider before using Toradol. This ensures it is appropriate for your specific condition.
Dosage Guidelines
- Follow the prescribed dosage strictly; typical adult doses range from 15 mg to 30 mg for injection, or 10 mg for oral tablets.
- Do not exceed a total of 40 mg per day for oral use; less may be recommended for your health status.
- Avoid using Toradol for longer than five days consecutively to reduce the risk of serious side effects.
Monitoring Your Health
- Monitor for signs of gastrointestinal bleeding, such as black or bloody stools or persistent abdominal pain.
- Check for any allergic reactions, including rash, itching, or difficulty breathing.
- Regularly review kidney function tests if used long-term, particularly in those with existing kidney issues.
If you have existing conditions like peptic ulcers, heart disease, or kidney problems, discuss alternative pain management options with your healthcare provider. Avoid combining Toradol with other NSAIDs or alcohol to prevent increased risk of side effects. Keeping a medication diary can help track dosages and any adverse reactions you might experience.