When managing ocular conditions like elevated intraocular pressure, consider Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution as a reliable option. This medication primarily acts as an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, effectively reducing aqueous humor production and enhancing uveoscleral outflow. Regular dosing twice daily ensures optimal results, making it a practical choice for patients.
Before incorporating Brimonidine into a treatment plan, assess the patient’s medical history for any contraindications or potential interactions. The solution is typically well-tolerated, but it’s wise to monitor for common side effects such as ocular hyperemia or dry mouth. Encouraging patients to report any unusual symptoms can aid in providing timely adjustments to their medication regimen.
For those using contact lenses, advise removing them before application and waiting at least 15 minutes to reinsert. Educating patients about the importance of proper technique during administration fosters adherence and maximizes therapeutic benefits. In instances where additional medications are necessary, a 5-10 minute interval between applications will minimize potential interactions.
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution serves as a valuable tool in glaucoma management, providing both efficacy and convenience. By following proper usage recommendations, patients can effectively control their symptoms and maintain optimal eye health.
- Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution: A Comprehensive Overview
- Mechanism of Action
- Dosing and Administration
- Mechanism of Action of Brimonidine Tartrate
- Indications and Uses in Ophthalmology
- Dosage Guidelines and Administration Techniques
- Application Steps
- Storage and Precautions
- Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
- Serious Side Effects
- Contraindications
- Comparative Efficacy with Other Antiglaucoma Medications
- Efficacy Compared to Prostaglandin Analogues
- Comparison with Beta-Blockers
- Recent Research and Future Developments in Brimonidine Therapy
- Latest Clinical Findings
- Future Developments
Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution: A Comprehensive Overview
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution provides targeted treatment for elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. This medication works by reducing aqueous humor production and enhancing uveoscleral outflow, facilitating effective management of eye pressure.
Mechanism of Action
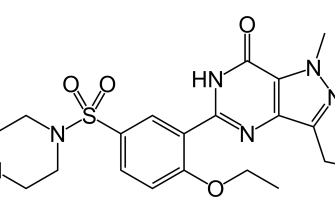
Brimonidine acts primarily as an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist. By stimulating alpha-2 receptors, it decreases adrenergic outflow and subsequently lowers aqueous humor production. Additionally, it promotes increased outflow through the uveoscleral pathway. These dual actions help maintain optimal intraocular pressure levels.
Dosing and Administration
The standard dosage for brimonidine tartrate is one drop in the affected eye(s) twice daily. Adhere to the following guidelines for safe usage:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Initial Dose | 1 drop in the affected eye(s) twice daily. |
| Administration | Apply drops in the conjunctival sac; avoid touching the dropper tip to any surface. |
| Missed Dose | If a dose is missed, apply it as soon as remembered unless it’s almost time for the next dose. |
| Storage | Store at room temperature; protect from light. |
Monitor for potential side effects such as dry mouth, fatigue, and conjunctival hyperemia. Regular follow-ups with an eye care professional are vital to assess intraocular pressure and adjust treatment as necessary.
This solution has demonstrated strong efficacy in lowering intraocular pressure and is a valuable component in glaucoma management. Prioritize adherence to prescribed dosing schedules for the best outcomes in ocular health.
Mechanism of Action of Brimonidine Tartrate
Brimonidine tartrate primarily acts as an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist. By binding to alpha-2 receptors in the ciliary body of the eye, it inhibits the release of norepinephrine, leading to a decrease in aqueous humor production. This results in a reduction of intraocular pressure (IOP), providing relief for patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
In addition to decreasing aqueous humor formation, brimonidine enhances uveoscleral outflow, further contributing to its IOP-lowering effects. This dual mechanism makes it particularly beneficial for patients who may not respond sufficiently to other treatments. With a direct impact on the receptors, brimonidine influences vasoconstriction and modulates ocular blood flow, helping to protect the optic nerve from damage associated with elevated pressure.
The medication is typically administered as an ophthalmic solution, which allows for targeted delivery with minimal systemic absorption. This localized action reduces the likelihood of systemic side effects while maximizing ocular efficacy.
When considering dosage, patients generally benefit from twice-daily administration. Adherence to this regimen is crucial for maintaining optimal IOP control. Regular follow-ups with an eye care professional ensure that patients’ responses to treatment are monitored and adjusted as necessary.
In summary, brimonidine tartrate’s unique mechanism–a combination of reduced aqueous humor production and increased outflow–offers a potent solution for managing intraocular pressure effectively.
Indications and Uses in Ophthalmology
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution is primarily indicated for the management of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It effectively reduces intraocular pressure by decreasing aqueous humor production and increasing uveoscleral outflow.
This medication is particularly advantageous for patients who experience side effects from other glaucoma therapies. Brimonidine’s dual mechanism of action allows for better intraocular pressure control while minimizing systemic absorption when used topically.
Additionally, it serves as a treatment option for patients with ocular redness due to its vasoconstrictive properties. By constricting blood vessels in the conjunctiva, it effectively reduces redness, making it appealing for cosmetic use as well.
Brimonidine is often included in treatment plans for patients requiring adjunctive therapy, especially those who have not achieved target pressure with other agents alone. Its compatibility with various other ophthalmic medications allows for flexible combination therapy.
Regular monitoring of intraocular pressure in patients using this solution is recommended to ensure optimal outcomes. Adjustments to therapy may be necessary based on individual response and tolerance.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Techniques
Administer Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution as prescribed by your healthcare provider. The standard dosing for adults is one drop in the affected eye(s) twice daily, approximately 12 hours apart. Adhere strictly to the recommended frequency to maintain the desired intraocular pressure control.
Application Steps
Start by washing your hands thoroughly. Tilt your head back and pull down your lower eyelid to create a small pocket. Hold the bottle upside down, and gently squeeze to instill one drop into the pocket. Avoid touching the tip of the bottle to your eye or any surface to prevent contamination.
After administration, close your eyes for a few moments and apply gentle pressure to the inner corner of your eye. This technique reduces systemic absorption and enhances local efficacy. Do not blink or rub your eye immediately after applying the drop.
Storage and Precautions
Store the solution at room temperature, away from light. Once opened, use within 28 days, discarding any remaining solution afterward. If you are using other eye medications, wait at least 5 to 10 minutes between applications. Inform your healthcare provider about any other medications you are taking to prevent interactions.
If you miss a dose, apply it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for the next dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and return to your regular schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up.
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution may cause several side effects. Commonly reported reactions include ocular hyperemia, burning, stinging, and blurred vision upon application. Patients may also experience headache, dry mouth, or sedation. Monitor for these effects, and consult a healthcare professional if they persist or worsen.
Serious Side Effects
In rare cases, patients might experience allergic reactions such as rash, itching, or swelling of the face and throat. Immediate medical attention is crucial for any signs of severe allergic responses. Additionally, brimonidine can lead to significant changes in heart rate and blood pressure in susceptible individuals, particularly those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
Contraindications
Brimonidine is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components. It should not be used in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or those with significant cardiovascular diseases. Caution is advised for individuals with depression, as brimonidine may exacerbate symptoms. Always review medical history with a healthcare provider to ensure safety during treatment.
Comparative Efficacy with Other Antiglaucoma Medications
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution demonstrates significant effectiveness in lowering intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Its action as an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist effectively reduces aqueous humor production while enhancing uveoscleral outflow.
Efficacy Compared to Prostaglandin Analogues
Prostaglandin analogues, such as latanoprost and bimatoprost, are often first-line therapies due to their robust IOP-lowering capabilities. Studies indicate that brimonidine may offer comparable reductions in IOP, particularly in patients who experience side effects from prostaglandin therapy. Data shows brimonidine achieves a reduction of about 20-25% in IOP.
Comparison with Beta-Blockers
When compared with beta-blockers like timolol, brimonidine similarly lowers IOP, often with fewer systemic side effects. While both classes can provide substantial pressure reduction, brimonidine is particularly beneficial for patients who may suffer from respiratory conditions, as beta-blockers can exacerbate these issues. Clinical trials report similar pressure-lowering efficacy between these medications, affirming their roles in treatment regimens.
In summary, brimonidine tartrate presents a valuable option in the antiglaucoma arsenal, especially for patients requiring alternative therapies. Its unique mechanism of action, in conjunction with its efficacy relative to other medications, supports its inclusion in glaucoma management strategies. Individual patient factors should guide the choice of therapy to optimize outcomes.
Recent Research and Future Developments in Brimonidine Therapy
Recent studies have highlighted the enhancement of intraocular pressure (IOP) control in glaucoma patients through the use of Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution. A clinical trial demonstrated significant IOP reduction compared to baseline values at various time intervals post-administration.
Latest Clinical Findings
One promising finding is the long-term safety profile of Brimonidine, particularly in patients previously treated with other therapies. Research shows a lower incidence of systemic side effects, making it suitable for a broader patient base.
- Patients report improved tolerability and satisfaction rates.
- Studies indicate Brimonidine reduces the progression of visual field defects.
- Combination therapies with other classes of glaucoma medications show potential for synergistic effects without increased side effects.
Future Developments
Looking ahead, researchers are exploring novel drug delivery systems to enhance Brimonidine’s efficacy. Sustained-release formulations are under investigation, promising better adherence and prolonged therapeutic effects.
- Microneedle patches for transdermal delivery are being developed to bypass ocular barriers.
- Instillation devices that optimize dosing may increase patient compliance.
- Targeted therapies using nanoparticles are also being researched.
Continued exploration of Brimonidine’s role in managing ocular conditions beyond glaucoma is underway. These innovative approaches stand to improve patient outcomes significantly, reinforcing the ongoing relevance of Brimonidine therapy in ophthalmology.